3. Python Package Ecosystem
Welcome back to the Python for Cybersecurity web series!
In the first lesson, we saw that Python is predominantly used in cybersecurity because of the powerful packages it has to offer. So, what are those? A gist of the most sought-after packages can be found in this post — Most sought after Python packages.
What we are going to do in this lesson is to try and understand how to use a few of the packages related to security by reviewing and implementing simple code constructs in Python.Source: https://www.caktusgroup.com/blog/2016/03/17/best-python-libraries/

Learning Goals
Learn about the useful packages in Python for cybersecurity
Be able understand those packages through simple programming constructs
Practice exercise based on the packages
Learning Time — 2 hours
1. Faker
Let us start with a very simple one! As the name says, Faker is a package that helps to create fake and random data. But, how is that useful? Where testing plays an essentially major role, Faker can be useful to generate test and random data. Many companies use this package to run automation testing and stress testing their software and applications.
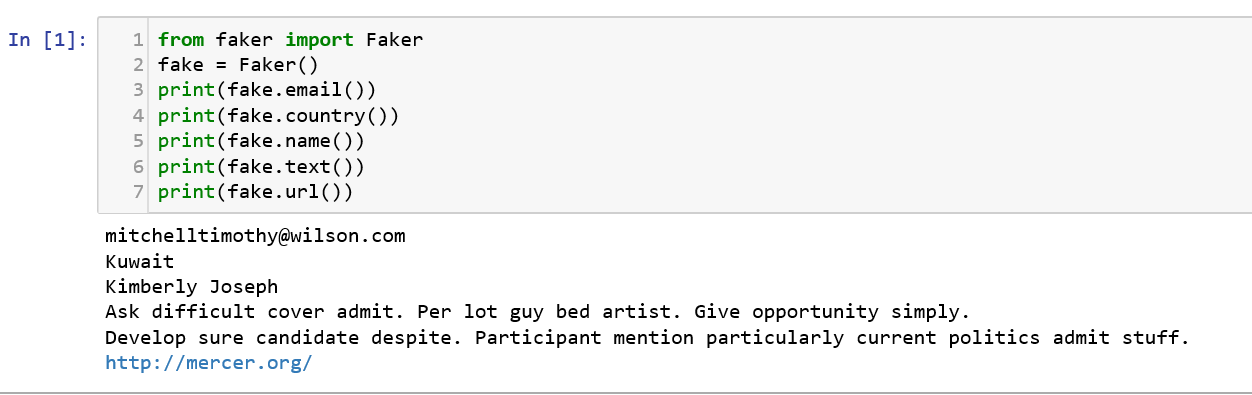
Practice
Generate a fake address with latitude and longitude using faker.
2. NumPy
NumPy is predominantly used in analyzing numerical data and it provides a powerful N-dimensional array object that has sophisticated functions to accommodate the computational capabilities. Let us see a very simple example of using numpy to generate a random number array.
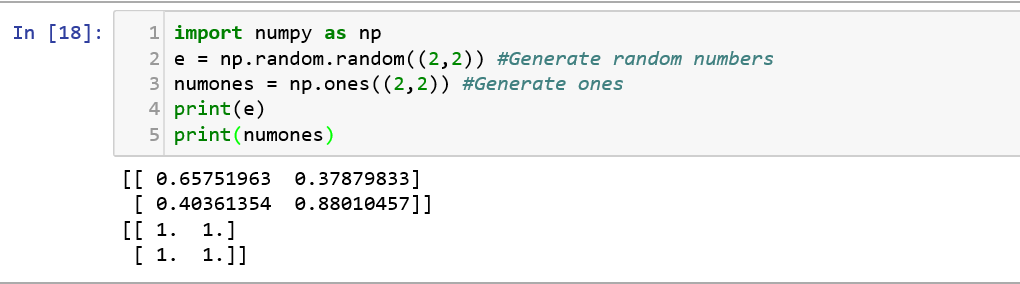
Recollect that the NumPy declaration is very similar to the array declaration in Python, but it is much more sophisticated in terms of mathematical computation capabilities. Let us try to understand how helpful NumPy is.
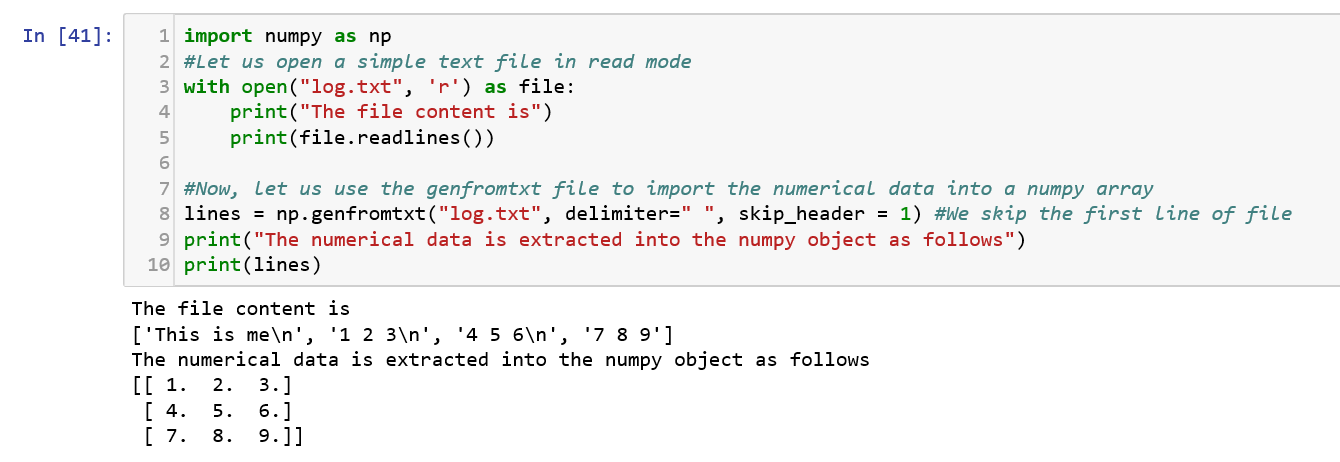
As you can see in the above example, NumPy facilitates reading the numerical data from a file into an array which is the first step when trying to perform data analysis.
Practice
Read a text file into NumPy array and see what happens!
3. Scipy
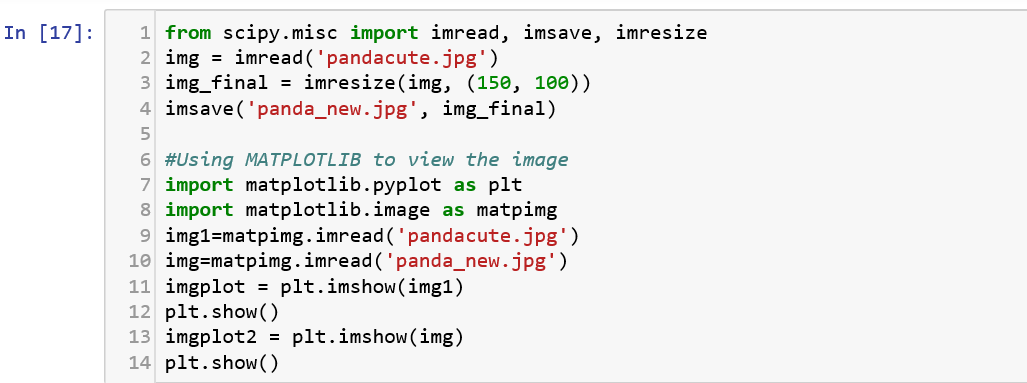
From performing simple file I/O operations to performing image processing and statistical analysis, Scipy is one of the most powerful packages available in Python. It was built to work along with Numpy to be used for numerical manipulations. It aids a lot in incorporating data analysis with cybersecurity. Let us see a simple example where we use scipy to read an image and resize it.
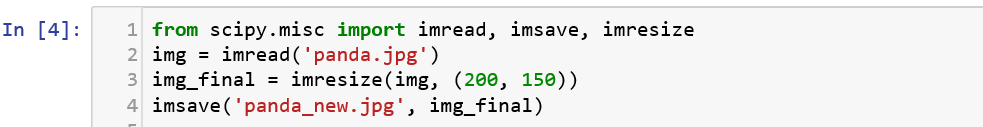
The code here reads the image using imread(), resizes the image using the imreseize() function and saves it to your present directory using imsave().
Practice
Implement the above code using skimage package which works similarly.
4. Matplotlib
This 2D Python library is the most widely used visualization tool because of its ability to generate histograms, charts and plots with very few lines of code. It can basically help you analyze the data through visual aids. This can be understood better if we try to visualize an example. Let us try to display the above images that we read and saved in Scipy.
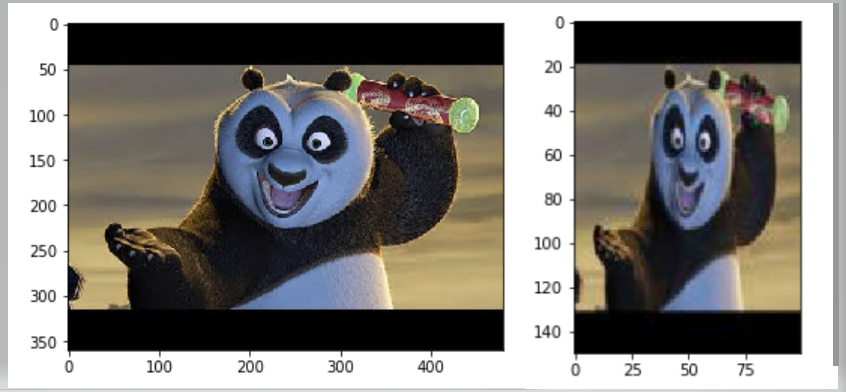
You can see that the image on the right is resized according to the specified dimensions. This specific feature is really helpful when analyzing images using deep learning where having uniform size of images gives you better results.
Practice
Plot numbers 1–5 using matplotlib.pyplot package and display the plot.
5. Nmap
Nmap is an open source utility used for network discovery. Nmap uses raw IP packets to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services (application name and version) those hosts are offering, what operating systems (and OS versions) they are running, what type of packet filters/ firewalls are in use, and more. Let us see a simple implementation yet one of the most useful recon tools — Port Scanner. We implement what the nmap command does, using the following code in Python.
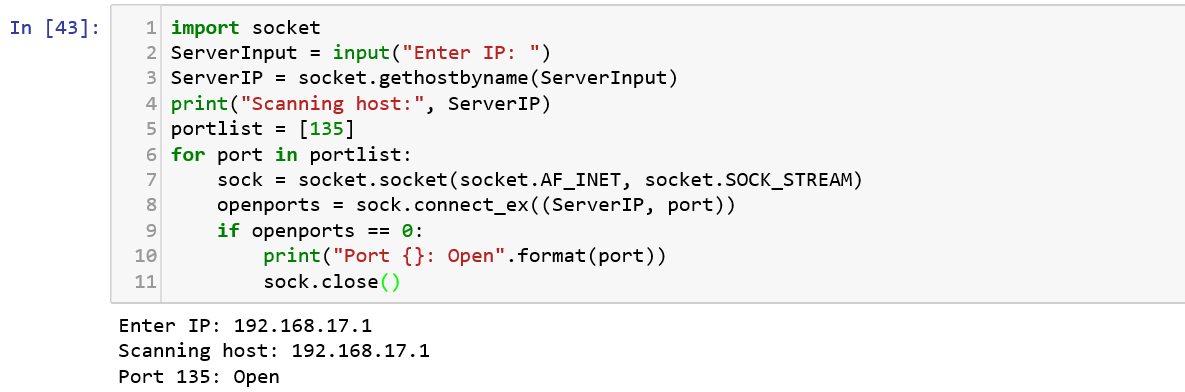
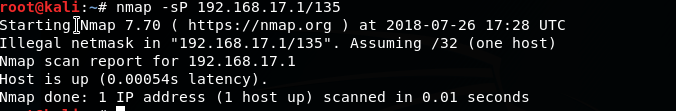
Practice
Scan through a list of “Well-Known” ports and see which ones are open.
6. Pandas
This is one of the most widely used data analysis tools in Python which provides the ability to manipulate datasets required for training, modeling and analysis in machine learning. According to towardsdatascience.com, Pandas is generally used to:
Convert a Python’s list, dictionary or Numpy array to a Pandas data frame
Open a local file using Pandas, usually a CSV file, but could also be a delimited text file (like TSV), Excel, etc
Open a remote file or database like a CSV or a JSONon a website through a URL or read from a SQL table/database
Let us try to import a text file in fixed file format using pandas.
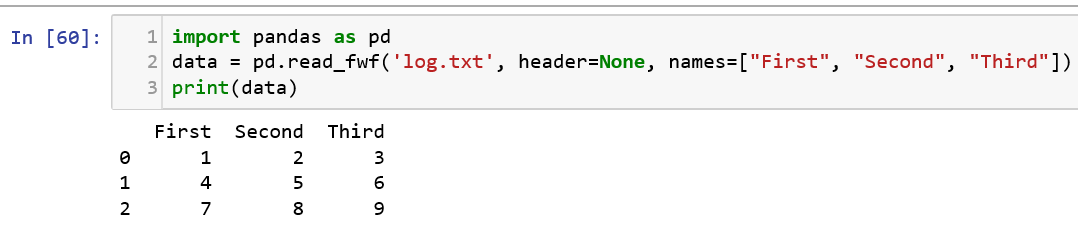
Practice
Add an attribute to skip the first row of data when displaying the content.
7. Beautiful Soup
This package was designed for the Python programming language and it parses anything you give it. It does the tree traversal for the user and scrapes the HTML and XML files for information specified to be looked up for. It is used to simulate the data which can be retrieved from a client’s website and secure the channel. Let us see how BS4 can be used to retreive information.
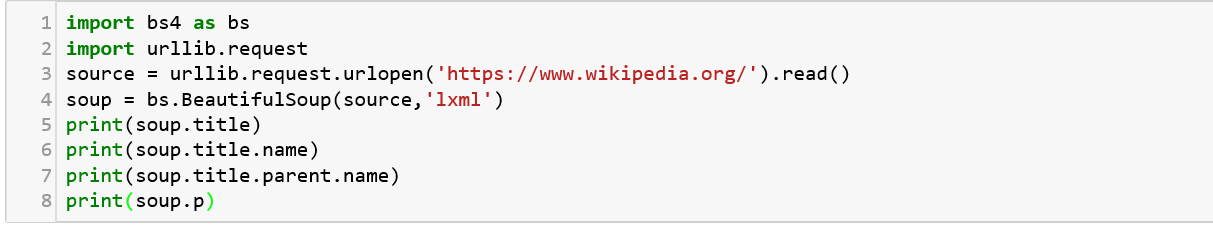
As we can see, the source URL is specified which is then parsed through ‘soup’ and broken into title and name. Similarly, many other functions can be implemented on this to extract specific information as per need for defending an application from attacks. Another similar package to be looked into is Scrapy, which is used for a little advanced version known as web crawling.
Practice
Try to ‘find all’ the links (hrefs) from any one of the Wikipedia pages.
8. Cryptography
This package includes both high level and low level interfaces to common cryptographic algorithms such as symmetric ciphers, message digests, and key derivation functions. Here, a Fernet is an implementation of symmetric (also known as “secret key”) authenticated cryptography which guarantees that a message encrypted using it cannot be manipulated or read without the key. Let us try to encrypt and decrypt a message using this package function:
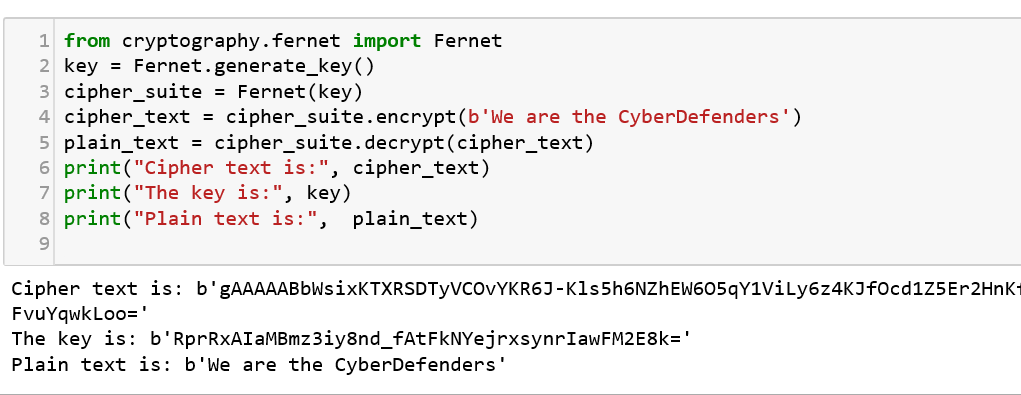
Practice
Implement MultiFernet to use multiple keys for encryption/decrytion process.
9. Twisted
Twisted is an open source, event-driven networking engine that supports many common transport and application layer protocols, including TCP, UDP, SSL/TLS, HTTP, IMAP, SSH, IRC, and FTP. It comes with client and server implementations for all of its protocols which makes it easier to deploy and configure. Let us see a sample implementation of twisted that echoes every user input when connected using a telnet.

When connected through a telnet client to the server, the messages sent get echoed.![]()

As you can see, the server code on the top just listens to whatever data is transferred and displays the same.
Practice
Implement a similar program for the client side to print the messages in a different format.
10. Scapy
This package, which is one of the most powerful network analysis package, is a packet manipulation library where forging or decoding packets for a wide number of protocols, sending them on the wire, capturing them and much more can be done. Scapy tries to use default values for all the packet fields.

This will sniff the network for 10 packets and once they have been sniffed, it will print their summary.
Practice
Construct and send a packet to a specific destination of your choice.
These are a few of the powerful packages and their implementations that Python has to offer. Try to implement the practice problems and gain familiarity with the packages to be able to build off of it in the later part of the course. Keep looking and learning other packages that Python has to offer to make lives easier and secure.
Do you know of any other interesting packages in Python? Leave a comment below!
Happy Learning!!
Additional learning resources
This site offers a wide range of libraries primarily used for security. You should be able to explore a lot here: http://www.pythonsecurity.org/libs
Last updated